Borosilicate glass
In this text you will learn about borosilicate glass: properties, strength, thermal and chemical resistance, types, and applications in laboratory, industrial, optical, and domestic environments.
Properties and applications of borosilicate glass
Borosilicate glass is a specialized type of glass that contains significant amounts of silica (SiO₂) and boron trioxide (B₂O₃), making it highly resistant to thermal shock and chemical corrosion. Known for its durability, clarity, and stability under temperature fluctuations, borosilicate glass is widely used in laboratory, industrial, and domestic applications. Often referred to as boro glass, this material exhibits unique performance characteristics that set it apart from conventional soda-lime glass.
One of the key properties of borosilicate glass is its exceptional resistance to temperature changes. This heat resistant glass can withstand both extremely high and low temperatures, making it suitable for demanding environments. The borosilicate glass temperature resistance allows it to endure up to 450 °C during long-term use and down to -196 °C when in contact with substances like liquid nitrogen. These attributes are a result of its low coefficient of thermal expansion, which ensures the glass does not crack or deform when exposed to rapid temperature changes.
Another significant feature is the borosilicate glass strength and durability under mechanical and thermal stress. The typical hardness of borosilicate glass is rated at 5.5 on the Mohs scale, with corresponding values of 470 on the Knoop scale and 580 on the Vickers hardness test. These measures confirm the high borosilicate glass hardness, making it ideal for situations that demand both precision and resilience.
The versatility of borosilicate glass arises from the ability to modify its chemical composition by incorporating various metal oxides. These variations result in a broad range of borosilicate glass products, each tailored for specific applications. The boron oxide content in the glass batch—i.e., the mix of raw materials used in the production process—plays a crucial role in defining not only the borosilicate glass properties, but also the behavior of the molten glass during manufacturing.
At our facility, we offer several types of borosilicate glass, including:
- Borosilicate glass 3.3 (DIN 7080)
- Borosilicate glass 4.3
- Suprax 8488
- Pyrex
- Boronorm
- Borofloat
Each of these borosilicate glass types features unique compositions and is suited for various borosilicate glass applications, from laboratory glassware and cookware to high-performance optics and chemical equipment.
Borosilicate glass 3.3 - DIN 7080
Borosilicate glass 3.3 is one of the most commonly used and well-known types of heat resistant glass. Its high silica content and significant boron oxide doping make it exceptionally stable. The material can be milled, drilled, ground, and toughened without losing its structural integrity. These characteristics, combined with its borosilicate glass strength, make it suitable for both industrial and scientific uses.
This type of boro glass performs reliably at elevated temperatures and is thermally stable up to 450 °C under continuous use. Its borosilicate glass temperature stability is a primary reason why it is frequently selected for laboratory setups and chemical reactors. Additionally, borosilicate glass 3.3 maintains excellent mechanical strength even in low-temperature conditions, with operational capability down to -196 °C, making it compatible with cryogenic substances like liquid nitrogen. For optimal safety, the temperature difference during thawing should not exceed 100 K; typically, operation down to -70 °C is recommended.
Thanks to its outstanding chemical resistance, this borosilicate glassware is impervious to water, acids, alkalis, and most organic solvents. As such, it is extensively used in pharmaceutical manufacturing, scientific research, and chemical processing plants. The borosilicate glass properties of type 3.3 also make it a material of choice for borosilicate glass dishes, beakers, flasks, and other laboratory vessels.
Suprax 8488, Pyrex, Boronorm & Borofloat
Other types of borosilicate glass, such as Suprax 8488, Pyrex, and Boronorm, offer comparable borosilicate glass hardness and resistance to chemical and thermal stresses. Suprax 8488 is known for its consistency and is often used in technical lighting and optical applications. Pyrex, a widely recognized brand name, is commonly found in consumer borosilicate glass products like cookware and bakeware. These borosilicate glass dishes resist staining, cracking, and thermal deformation, making them ideal for use in ovens and microwave environments.
Borofloat is another premium borosilicate glass variant designed for optical, display, and semiconductor applications. Its exceptionally smooth surface and excellent flatness, combined with its inherent borosilicate glass strength, make it indispensable in high-tech industries. Whether used in analytical instruments or microelectronics, Borofloat ensures consistent performance under stress.
Applications of borosilicate glass
The variety of borosilicate glass applications is as vast as its properties. It is widely used in:
- Laboratory borosilicate glassware (beakers, test tubes, measuring cylinders)
- Domestic borosilicate glass products (bakeware, cookware, coffee carafes)
- Pharmaceutical containers (vials, ampoules)
- Chemical processing equipment (reactors, pipelines)
- Optical components (lenses, filters)
- High-intensity lighting systems (projector lamps, automotive bulbs)
- Solar energy systems (glass tubing, photovoltaic module covers)
- Display technology (substrates for TFT and OLED displays)
The heat resistance of glass in these applications is crucial for maintaining dimensional stability and ensuring longevity. For instance, borosilicate glass dishes used in kitchens can transition directly from freezers to ovens without risk of breakage due to the material’s thermal shock resistance.
Why choose borosilicate glass?
To summarize, borosilicate glass combines chemical inertness, high mechanical strength, and remarkable temperature resistance, making it one of the most versatile materials available. Its hardness, clarity, and processability further enhance its desirability across numerous industries. Whether you are selecting materials for a high-performance optical lens, a laboratory flask, or a heat-resistant baking dish, borosilicate glass delivers outstanding performance.
We supply a full range of borosilicate glassware and custom borosilicate glass products tailored to your specific needs. With several types of borosilicate glass available, including borosilicate glass 3.3, Suprax, Borofloat, and Pyrex, our product line meets the highest standards in modern engineering and design.
Borosilicate glass 3.3 - DIN 7080
Composition
| SiO2 | 80 % |
| B2O3 | 13 % |
| Na2O | 4 % |
| Al2O3 | 2 % |
| K2O | 1 % |
Standard thicknesses and tolerances
| Thickness | Tolerance | Thickness | Tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0,70 mm | ±0,1 | 7,5 mm | ±0,3 |
| 1,10 mm | ±0,1 | 8,0 mm | ±0,3 |
| 1,75 mm | ±0,2 | 9,0 mm | ±0,3 |
| 2,00 mm | ±0,2 | 13,0 mm | ±0,5 |
| 2,25 mm | ±0,2 | 15,0 mm | ±0,5 |
| 2,75 mm | ±0,2 | 16,0 mm | ±0,5 |
| 3,30 mm | ±0,2 | 17,0 mm | ±0,5 |
| 5,00 mm | ±0,2 | 18,0 mm | ±0,5 |
| 5,50 mm | ±0,2 | 19,0 mm | ±0,5 |
| 6,50 mm | ±0,2 | 21,0 mm | ±0,7 |
Properties:
| Density (@ 20 °C) | 2 230 kg/m3 |
| Bending strength | 160 N/mm2 |
| Surface compressive stress | 100 N/mm2 |
| Young’s modulus | 64 GPa |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0,2 |
| Hardness | 5.5 Mohs, (470 Knopp, 580 Vickers) |
| Thermal conductivity | 1,2 W/(m K) |
| Specific Heat | 0,83 kJ/(kg K) |
| Coefficient of linear expansion | 3,3 ±0,1 * 10 -6 °C |
| Index of refraction (@ 380 - 780 nm) | 1,48 |
| Softening point | 815 °C |
| Annealing Point | 560 °C |
| Max. working temperature: | |
| Non-tempered glass | |
| - long term | 450 °C |
| - temporary(< 10h) | 500 °C |
| Tempered glass | |
| - long term | 280 °C |
| - temporary(< 10h) | 500 °C |
Chemical properties:
Hydrolytic Resistance
Acc. ISO 719 (w 98 °C): class HGB 1
Acc. ISO 720 (w 121 °C): class HGA 1
Alkali resistance
Acc. DIN 52 322 (ISO 695): class A2
Acid resistance
Acc. DIN 12 116: class 1
Electrical properties
Volume resistance
at 25°C = 6.6 x 1013 Ω cm
at 300°C = 1.4 x 106 Ω cm
Dielectric properties
| Electric Volume Resistivity | 8,6 x 1013 Ωcm | (at 25 °C) | |
| 1.4 x 106 Ωcm | (at 300 °C) | ||
| Dielectric dissipation fraction | 38 10-4 | (at 1 MHz, 20 °C) | |
| Dielectric constant εr | 4.6 | (at 1 MHz, 20 °C) |
Optical properties
| Index of Refraction |
Spectral Transmission |
| λ = 587,6 nm nD = 1,4724 λ = 480,0 nm nF = 1,4782 λ = 546,0 nm nE = 1,4740 λ = 644,0 nm nC = 1,4701 |
 |
Borosilicate glass 4.3
| SiO2 | 78 % |
| B2O3 | 10% |
| Na2O | 7 % |
| Al2O3 | 3% |
| ZrO2 | 2 % |
Properties:
| Density (@ 25 °C) | 2 280 kg/m3 |
| Flexural strength | 25 MPa |
| Modulus of elasticity (Young’s) | 67 GPa |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0,20 |
| Thermal conductivity (@ 90 °C) | 1,2 W/(m K) |
| Specific heat | 0,83 kJ/(kg K) |
| Coefficient of linear expansion (@ 20 °C - 300 °C) | 4,3 * 10 -6 °C |
| Index of Refraction (λ=587,6 nm) | 1,484 |
| Softening point | 810 °C |
| Annealing point | 580 °C |
| Glass temperature for density dPas |
1013,0 560 °C |
| Working temperature: | |
| - maximum | 500 °C |
| - in a heavy duty conditions | 280 °C |
Chemical properties
Hydrolytic Resistance
Acc. ISO 719 (@ 98 °C): class HGB 1
Acc. ISO 720 (@ 121 °C): class HGA 1
Alkali resistance
Acc. DIN 52 322 (acc. ISO 695): class A2
Acid resistance
Acc. DIN 1776: class 1
Electrical properties
Volume resistance
@ 25°C = 6.6 x 1013 Ω cm
@ 300°C = 1.4 x 106 Ω cm
Dielectric properties
@ 25° C and 1 MHz:
Dielectric constant εr=4,6
Dielectric loss factor tgδ =1,4x10-2
Optical properties
| Index of Refraction | Spectral Transmission |
| λ = 587,6 nm nD = 1,4816 λ = 480,0 nm nF = 1,4869 λ = 546,0 nm nE = 1,4831 λ = 644,0 nm nC = 1,4802 |
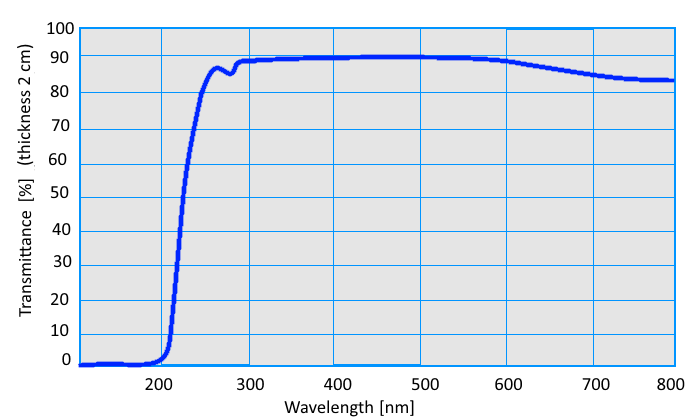 |
While every attempt has been made to verify the source of the information, no responsibility is accepted for accuracy of data.





